Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ5.5(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.01mm |
| Roundness | 0.003mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.4 |
| Straightness | 0.008mm |
| Hardness | HRC45-50 |
| Length | 60mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do spline shafts contribute to efficient power transmission?
Spline shafts play a vital role in enabling efficient power transmission in various mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how spline shafts contribute to efficient power transmission:
1. Torque Transmission:
Spline shafts are designed to transmit torque from one component to another. They provide a positive, non-slip connection that allows for efficient power transfer without slippage or loss of energy. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating a strong mechanical connection for torque transmission.
2. Load Distribution:
Spline shafts distribute the applied load evenly across the engagement surfaces. The teeth or grooves on the shaft’s spline profile ensure that the load is shared across multiple contact points. This even load distribution helps prevent localized stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. Efficient load distribution ensures that power is transmitted smoothly and reliably.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline shafts can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment between the mating components. The spline profile design allows for angular or parallel misalignment without compromising the power transmission capability. This misalignment compensation capability is crucial in maintaining efficient power transmission in situations where perfect alignment is challenging or subject to variations.
4. High Torque Capacity:
Spline shafts are designed to withstand high torque levels. The spline profile, engagement length, and material selection are optimized to handle the expected torque requirements. This high torque capacity ensures that the shaft can efficiently transmit power without experiencing excessive deflection or failure under normal operating conditions.
5. Torsional Stiffness:
Spline shafts exhibit high torsional stiffness, which means they resist twisting or torsional deflection when subjected to torque. The shaft’s design, including its diameter, spline profile, and material properties, contributes to its torsional stiffness. High torsional stiffness minimizes power loss due to deformation or flexing of the shaft, allowing for efficient power transmission.
6. Reliable Connection:
Spline shafts provide a reliable and repeatable connection between the driving and driven components. Once properly engaged, the spline shaft maintains its connection, ensuring consistent power transmission over time. This reliability is crucial in maintaining efficiency and preventing power loss or interruptions during operation.
7. Minimal Backlash:
Backlash refers to the slight rotational play or clearance between mating components. Spline shafts, when properly designed and manufactured, can minimize backlash in the power transmission system. Reduced backlash ensures smoother operation, improved accuracy, and efficiency by minimizing power losses associated with reversing or changing direction.
8. Compact Design:
Spline shafts offer a compact and space-efficient solution for power transmission. Their design allows for a relatively small footprint while providing robust torque transmission capabilities. The compact design is particularly advantageous in applications where space is limited, such as automotive drivetrains or compact machinery.
By incorporating spline shafts into mechanical systems, engineers can achieve efficient power transmission, ensuring that power is effectively transferred from the driving source to the driven components. The unique design features of spline shafts enable reliable torque transmission, even load distribution, misalignment compensation, high torque capacity, torsional stiffness, reliable connections, minimal backlash, and compactness.
Can spline shafts be used in automotive applications, and if so, how?
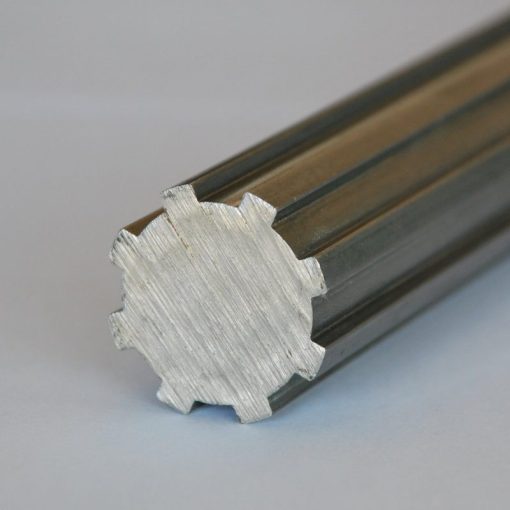
Yes, spline shafts are extensively used in automotive applications due to their ability to transmit torque and provide reliable power transmission. Here’s how spline shafts are used in automotive applications:
Spline shafts play a crucial role in various automotive systems and components, including:
- Drivetrain: Spline shafts are an integral part of the drivetrain system in vehicles. They transmit torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move. Spline shafts are present in components such as the transmission, differential, and axle shafts. In manual transmissions, the spline shaft connects the transmission input shaft to the clutch disc, enabling power transfer from the engine. In automatic transmissions, spline shafts are used in the torque converter and the output shaft.
- Steering System: Spline shafts are employed in the steering system to transmit torque from the steering wheel to the steering rack or gearbox. They provide a direct connection between the driver’s input and the movement of the wheels, allowing for steering control.
- Power Take-Off (PTO) Systems: Some vehicles, particularly commercial trucks and agricultural machinery, utilize PTO systems. Spline shafts are used in PTOs to transfer power from the vehicle’s engine to auxiliary equipment, such as hydraulic pumps, generators, or agricultural implements.
- Transfer Cases: In four-wheel-drive (4WD) or all-wheel-drive (AWD) vehicles, transfer cases are used to distribute power to the front and rear axles. Spline shafts are utilized in the transfer case to transfer torque between the transmission and the front and rear drive shafts.
- Propeller Shafts: Spline shafts are present in propeller shafts, which transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle in rear-wheel-drive vehicles. They accommodate the relative movement between the transmission and the axle due to suspension travel.
In automotive applications, spline shafts are designed to withstand high torque loads, provide precise torque transmission, and accommodate misalignments and fluctuations in operating conditions. They are typically made from high-strength steel or alloy materials to ensure durability and resistance to wear. Proper lubrication is essential to minimize friction and ensure smooth operation.
The use of spline shafts in automotive applications allows for efficient power transmission, precise control, and reliable performance, contributing to the overall functionality and drivability of vehicles.

What is a spline shaft and what is its primary function?
A spline shaft is a mechanical component that consists of a series of ridges or teeth (called splines) that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. Its primary function is to transmit torque while allowing for the relative movement or sliding of mating components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Structure and Design:
A spline shaft typically has a cylindrical shape with external or internal splines. The external spline shaft has splines on the outer surface, while the internal spline shaft has splines on the inner bore. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the specific application and design requirements.
2. Torque Transmission:
The main function of a spline shaft is to transmit torque between two mating components, such as gears, couplings, or other rotational elements. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating a mechanical interlock. When torque is applied to the spline shaft, the engagement between the splines ensures that the rotational force is transferred from the shaft to the mating component, allowing the system to transmit power.
3. Relative Movement:
Unlike other types of shafts, a spline shaft allows for relative movement or sliding between the shaft and the mating component. This sliding motion can be axial (along the shaft’s axis) or radial (perpendicular to the shaft’s axis). The splines provide a precise and controlled interface that allows for this movement while maintaining torque transmission. This feature is particularly useful in applications where axial or radial displacement or misalignment needs to be accommodated.
4. Load Distribution:
Another important function of a spline shaft is to distribute the applied load evenly along its length. The splines create multiple contact points between the shaft and the mating component, which helps to distribute the torque and axial or radial forces over a larger surface area. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure.
5. Versatility and Applications:
Spline shafts find applications in various industries and systems, including automotive, aerospace, machinery, and power transmission. They are commonly used in gearboxes, drive systems, power take-off units, steering systems, and many other rotational mechanisms where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are essential.
6. Design Considerations:
When designing a spline shaft, factors such as the torque requirements, speed, applied loads, and environmental conditions need to be considered. The spline geometry, material selection, and surface finish are critical for ensuring proper engagement, load-bearing capacity, and durability of the spline shaft.
In summary, a spline shaft is a mechanical component with splines that allows for torque transmission while accommodating relative movement or sliding between mating components. Its primary function is to transmit rotational force, distribute loads, and enable axial or radial displacement in various applications requiring precise torque transfer and flexibility.


editor by CX 2024-05-08
China Hot selling Automotive Spline Shaft ODM/OEM CNC Machining Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Knurling/Grinding with Black Treatment for Transmissions/Gearboxes Drive Worm
Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High-precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings,……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, spline shafts, and stepped shafts that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ5.5(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.01mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.4 |
| Straightness | 0.008mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 60mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial order are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Customized |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | CE, DIN, ISO |
| Type: | C.V. Joint |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Iveco, Toyota, Ford |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
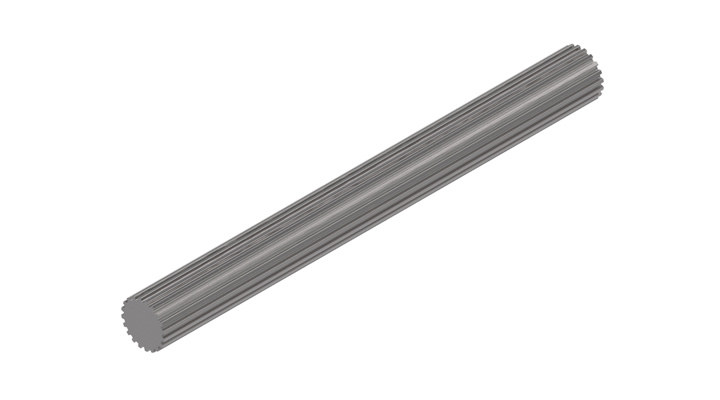

Can spline shafts be customized for specific machinery and equipment?
Yes, spline shafts can be customized to suit specific machinery and equipment requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Size and Length:
Spline shafts can be customized in terms of size and length to fit the dimensions of the machinery or equipment. Manufacturers can design spline shafts with the appropriate diameter, overall length, and spline length to ensure a proper fit within the system.
2. Spline Profile:
The spline profile can be customized based on the specific application. Different spline profiles, such as involute, serrated, or helical, can be used to optimize torque transmission, load distribution, and engagement characteristics based on the requirements of the machinery or equipment.
3. Number of Splines:
The number of splines on the shaft can be customized to match the mating component. The number of splines determines the engagement area and affects the torque-carrying capacity of the spline shaft. By adjusting the number of splines, manufacturers can tailor the spline shaft to the specific torque and load requirements of the machinery or equipment.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of material for spline shafts can be customized based on the operating conditions and environmental factors of the machinery or equipment. Different materials, such as alloy steels or stainless steels, can be selected to provide the necessary strength, durability, corrosion resistance, or other specific properties required for the application.
5. Surface Treatment:
The surface of spline shafts can be customized with various treatments to enhance their performance. Surface treatments like heat treatment, coating, or plating can be applied to improve hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance based on the specific requirements of the machinery or equipment.
6. Tolerances and Fit:
Tolerances and fit between the spline shaft and mating components can be customized to achieve the desired clearance or interference fit. This ensures proper engagement, smooth operation, and optimal performance of the machinery or equipment.
7. Special Features:
In certain cases, spline shafts can be customized with additional features to meet specific needs. This may include the incorporation of keyways, threads, or other specialized features required for the machinery or equipment.
Manufacturers and engineers work closely with the machinery or equipment designers to understand the specific requirements and tailor the spline shafts accordingly. By considering factors such as size, spline profile, number of splines, material selection, surface treatment, tolerances, fit, and any special features, customized spline shafts can be developed to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the machinery or equipment.
It is important to consult with experienced spline shaft manufacturers or engineering professionals to determine the most suitable customization options for a particular machinery or equipment application.

How do spline shafts handle variations in load capacity and weight?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in load capacity and weight in mechanical systems. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel or alloy, chosen for their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide durability. The selection of materials takes into account factors such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance to ensure the shaft can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
2. Engineering Design:
Spline shafts are designed with consideration for the anticipated loads and weights they will encounter. The dimensions, profile, and number of splines are determined based on the expected torque requirements and the magnitude of the applied loads. By carefully engineering the design, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight while maintaining structural integrity and reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution:
The interlocking engagement of spline shafts allows for effective load distribution along the length of the shaft. This helps distribute the applied loads evenly, preventing localized stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of deformation or failure. By distributing the load, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight without compromising their performance.
4. Structural Reinforcement:
In applications with higher load capacities or heavier weights, spline shafts may incorporate additional structural features to enhance their strength. This can include thicker spline teeth, larger spline diameters, or reinforced sections along the shaft. By reinforcing critical areas, spline shafts can handle increased loads and weights while maintaining their integrity.
5. Lubrication and Surface Treatment:
Proper lubrication is essential for spline shafts to handle variations in load capacity and weight. Lubricants reduce friction between the mating surfaces, minimizing wear and preventing premature failure. Additionally, surface treatments such as coatings or heat treatments can enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the spline shaft, improving its ability to handle varying loads and weights.
6. Testing and Validation:
Spline shafts undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet the specified load capacity and weight requirements. This may involve laboratory testing, simulation analysis, or field testing under real-world conditions. By subjecting spline shafts to thorough testing, manufacturers can verify their performance and ensure they can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
Overall, spline shafts are designed and engineered to handle variations in load capacity and weight by utilizing appropriate materials, optimizing the design, distributing loads effectively, incorporating structural reinforcement when necessary, implementing proper lubrication and surface treatments, and conducting thorough testing and validation. These measures enable spline shafts to reliably transmit torque and handle varying loads in diverse mechanical applications.
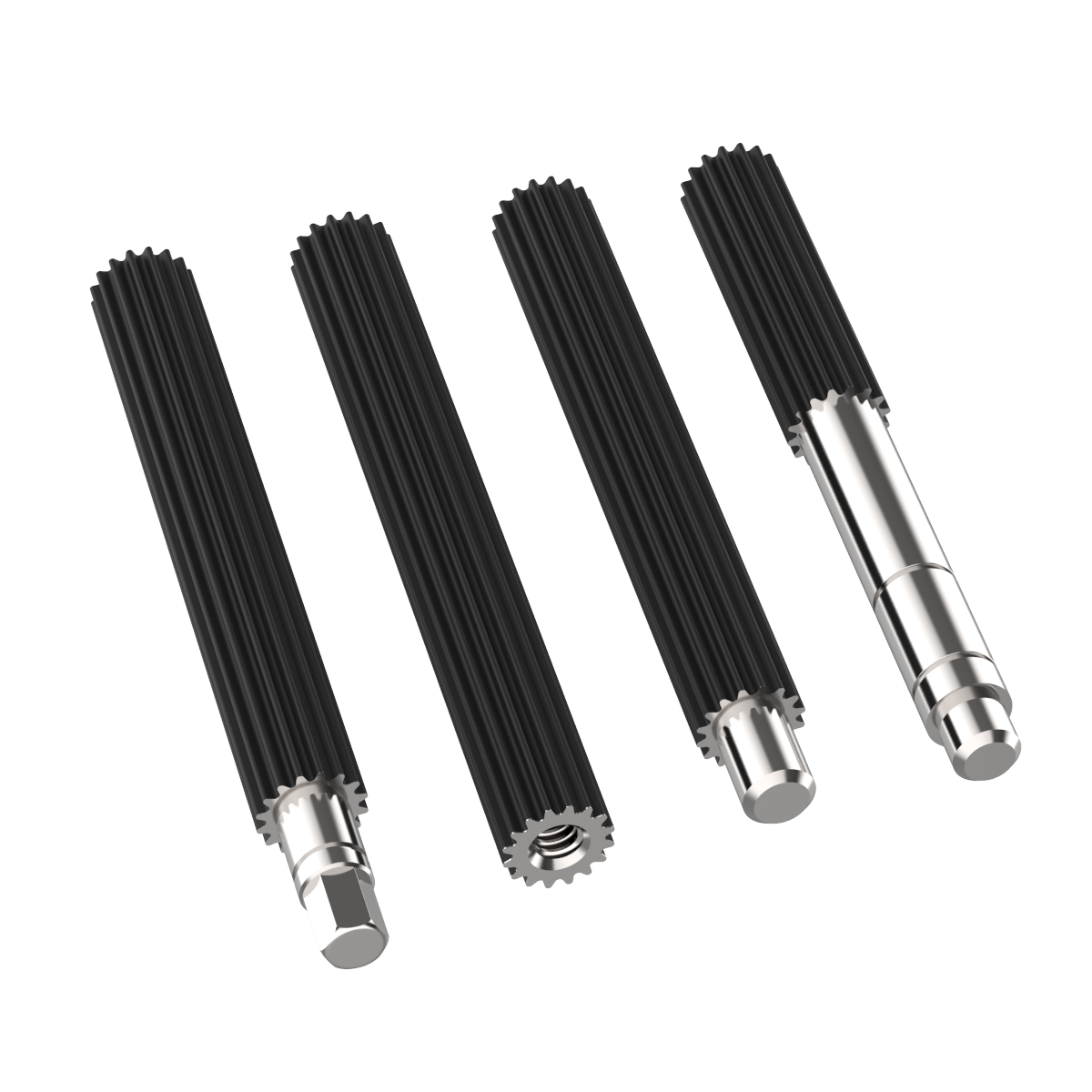

Can you explain the common applications of spline shafts in machinery?
Spline shafts have various common applications in machinery where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are essential. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Gearboxes and Transmissions:
Spline shafts are commonly used in gearboxes and transmissions where they facilitate the transmission of torque from the input shaft to the output shaft. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the gears, allowing for precise torque transfer and accommodating relative movement between the gears.
2. Power Take-Off (PTO) Units:
In agricultural and industrial machinery, spline shafts are employed in power take-off (PTO) units. PTO units allow the transfer of power from the engine to auxiliary equipment, such as pumps, generators, or farm implements. Spline shafts enable the torque transfer and accommodate the relative movement required for PTO operation.
3. Steering Systems:
Spline shafts play a crucial role in steering systems, especially in vehicles. They are used in steering columns to transmit torque from the steering wheel to the steering rack or gearbox. The splines on the shaft ensure precise torque transfer while allowing for the axial movement required for steering wheel adjustment.
4. Machine Tools:
Spline shafts find applications in machine tools such as milling machines, lathes, and grinding machines. They are used to transmit torque and enable the relative movement required for tool positioning, feed control, and spindle rotation. Spline shafts ensure accurate and controlled movement of the machine tool components.
5. Industrial Pumps and Compressors:
Spline shafts are utilized in various types of pumps and compressors, including centrifugal pumps, gear pumps, and reciprocating compressors. They transmit torque from the driver (such as an electric motor or an engine) to the impeller or rotor, enabling fluid or gas transfer. Spline shafts accommodate the axial or radial movement caused by thermal expansion or misalignment.
6. Printing and Packaging Machinery:
Spline shafts are integral components in printing and packaging machinery. They are used in processes such as web handling, where precise torque transmission and relative movement are required for tasks like tension control, registration, and material feeding. Spline shafts ensure accurate and synchronized movement of the printing and packaging elements.
7. Aerospace and Defense Systems:
In the aerospace and defense industries, spline shafts are utilized in various applications, including aircraft landing gear systems, missile guidance systems, and helicopter rotor systems. They enable torque transmission, accommodate relative movement, and ensure precise control in critical aerospace and defense mechanisms.
8. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Spline shafts are employed in construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and loaders. They are used in hydraulic systems to transmit torque from the hydraulic motor to the driven components, such as the digger arm or the bucket. Spline shafts enable efficient power transfer and allow for the articulation and movement of the equipment.
These are just a few examples of the common applications of spline shafts in machinery. Their versatility, torque transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate relative movement make them essential components in various industries where precise power transfer and flexibility are required.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China 2019 Hot Sale Factory Direct Sell Inflatable Shaft Pneumatic Expanding Air Shaft and Aluminum Spline Alloy Shaft Black Gun Steel with Great quality
Warranty: 1 Year
Applicable Industries: Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Home Use, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Advertising Company
Weight (KG): 8
Showroom Location: United States
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Marketing Type: Hot Product 2571
Warranty of core components: 1 Year
Core Components: Bearing
Structure: Eccentric
Material: stainless steel, Stainless Steel
Coatings: non
Torque Capacity: Custom-Making
Model Number: OEM
Process: cnc turning
| Product Name | Mechanical mental parts processing |
| Material | Iron, aluminum, steel Alloys, carbon steel, tool steels,Stainless Steel, copper, bronze,brass, plastic,ABS,Nylon, PC, PP, POM, Hardened Metals, HSS, or as per the customers’ requirements. |
| Dimensions | 1~1500mm , depend on the drawings. |
| Tolerence | ±0.005mm , depend on the drawings. |
| Heat treatment | Nitridation,Carbonization, Induction hardening,Flame surface quenching,Ageing treatment,Annealing,Normalizing,Quenching and Tempering etc. |
| Surface treatment | Polish, PVD/CVD coating, Galvanized, Electroplating, Spraying, Chromeplate,Painting, Anodizing aluminumand, Silk screen and so on. |
| Processing equipments | CNC machining center, CNC lathe, grinding machine, automatic lathe machine, conventional lathe machine, milling machine, drilling machine, EDM, wire-cutting machine, CNC bending machine etc. |
| Testing machine | Digital Height Gauge, caliper, Coordinate measuring machine, projection machine, roughness tester, hardness tester and so on. |
| Minimum order quantity | negotiable |
| Delivery | 7-15 days after T/T 30% deposit. |
| Payment | T/T 30% deposit ,and cash 70% before shipment |
| Application | Semiconductor laser device, Printing machine spare, Medical equipment, Vehicle production equipment,Industrial machine, Packing machine, Sewing machine ect. |
Machining
Assembly
Our Company FactoryOffice
QC room
Team
Packing & DeliveryPacking :We have 3 ways to packing, carton box, plastic box and wooden box, The most suitable packing will be choosed when delivery .Delivery : Maritime transport and Air transport( TNT, DHL, UPS, FEDEX).
1. Blister packing2. Blister packing3. Carton box or wooden box 1. EPE Packing2. Protect with cushioning.6. Plastic box or wooden box.FAQQ: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?A:30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.If you have another question, pls feel free to contact us as below:
Standard Length Splined Shafts
Standard Length Splined Shafts are made from Mild Steel and are perfect for most repair jobs, custom machinery building, and many other applications. All stock splined shafts are 2-3/4 inches in length, and full splines are available in any length, with additional materials and working lengths available upon request and quotation. CZPT Manufacturing Company is proud to offer these standard length shafts.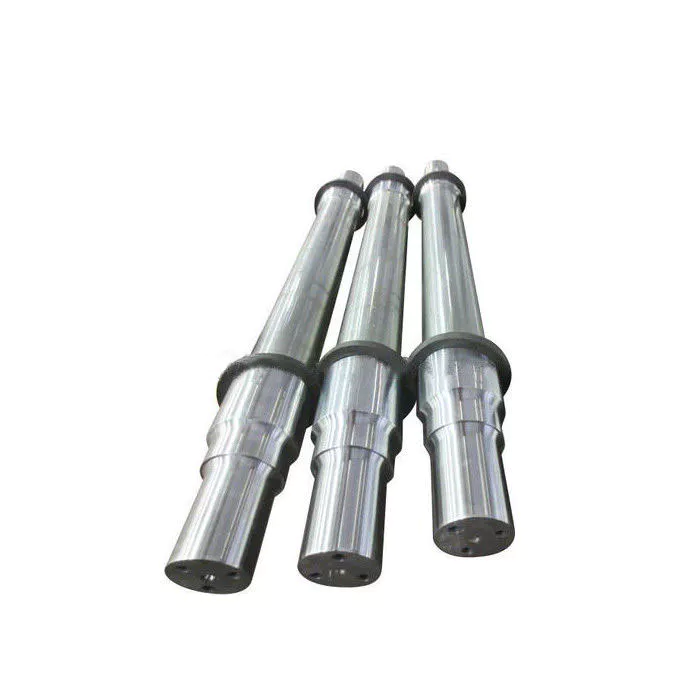
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are splined
There are two common disc brake mounting interfaces, splined and center lock. Disc brakes with splined interfaces are more common. They are usually easier to install. The center lock system requires a tool to remove the locking ring on the disc hub. Six-bolt rotors are easier to install and require only six bolts. The center lock system is commonly used with performance road bikes.
Post mount disc brakes require a post mount adapter, while flat mount disc brakes do not. Post mount adapters are more common and are used for carbon mountain bikes, while flat mount interfaces are becoming the norm on road and gravel bikes. All disc brake adapters are adjustable for rotor size, though. Road bikes usually use 160mm rotors while mountain bikes use rotors that are 180mm or 200mm.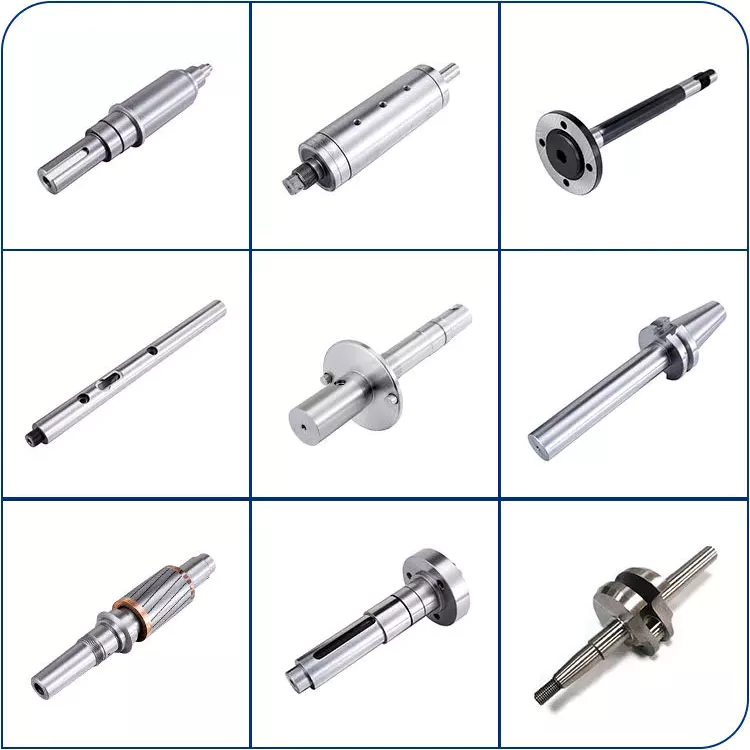
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined
A helical splined disc brake mounting interface is designed with a splined connection between the hub and brake disc. This splined connection allows for a relatively large amount of radial and rotational displacement between the disc and hub. A loosely splined interface can cause a rattling noise due to the movement of the disc in relation to the hub.
The splines on the brake disc and hub are connected via an air gap. The air gap helps reduce heat conduction from the brake disc to the hub. The present invention addresses problems of noise, heat, and retraction of brake discs at the release of the brake. It also addresses issues with skewing and dragging. If you’re unsure whether this type of mounting interface is right for you, consult your mechanic.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helix-splined may be used in conjunction with other components of a wheel. They are particularly useful in disc brake mounting interfaces for hub-to-hub assemblies. The spacer elements, which are preferably located circumferentially, provide substantially the same function no matter how the brake disc rotates. Preferably, three spacer elements are located around the brake disc. Each of these spacer elements has equal clearance between the splines of the brake disc and the hub.
Spacer elements 6 include a helical spring portion 6.1 and extensions in tangential directions that terminate in hooks 6.4. These hooks abut against the brake disc 1 in both directions. The helical spring portion 5.1 and 6.1 have stiffness enough to absorb radial impacts. The spacer elements are arranged around the circumference of the intermeshing zone.
A helical splined disc mount includes a stabilizing element formed as a helical spring. The helical spring extends to the disc’s splines and teeth. The ends of the extension extend in opposite directions, while brackets at each end engage with the disc’s splines and teeth. This stabilizing element is positioned axially over the disc’s width.
Helical splined disc brake mounting interfaces are popular in bicycles and road bicycles. They’re a reliable, durable way to mount your brakes. Splines are widely used in aerospace, and have a higher fatigue life and reliability. The interfaces between the splined disc brake and BB spindle are made from aluminum and acetate.
As the splined hub mounts the disc in a helical fashion, the spring wire and disc 2 will be positioned in close contact. As the spring wire contacts the disc, it creates friction forces that are evenly distributed throughout the disc. This allows for a wide range of axial motion. Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined have higher strength and stiffness than their counterparts.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helically splined can have a wide range of splined surfaces. The splined surfaces are the most common type of disc brake mounting interfaces. They are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum and can be used for a variety of applications. However, a splined disc mount will not support a disc with an oversized brake caliper.


editor by czh
China Professional Excavator Planetary Gear Shaft and Pinion Shaft Spline with High Strength Forging Material Black Oxide Nitriding HRC23-25 810mm carbon fiber drive shaft
Condition: New
Warranty: 1 Year
Applicable Industries: Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Construction works , Energy & Mining
Showroom Location: Brazil, Peru, Indonesia, Mexico, Russia, Thailand
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Marketing Type: New Product 2571
Warranty of core components: 1 Year
Core Components: Gear
Structure: Spline
Material: high strength 4330V, forging material 4330V
Coatings: Black Oxide
length: 810mm
Heat treatment: HRC23-25
Gear teeth surface hardening: Nitriding
Teeth surface hardness: HRC55-60
After Warranty Service: Video technical support, Online support, Spare parts
Local Service Location: Brazil, Peru, Indonesia, Mexico, Russia, Thailand, Australia, Chile, South Africa
Packaging Details: in wooden cases, as per customers’ requests
Port: ZheJiang Port
Products Description Planetary gear shaft and pinion shaft Material: 4330V forging material Size: φ600* Length 1000 mmNitriding Surface hardness : HRC55-60 Details Images Specification
| Brand Name | Eternal |
| length | 810mm |
| Material | forged 40CrNiMo |
| Heat treatment | HRC23-25 |
How to Calculate Stiffness, Centering Force, Wear and Fatigue Failure of Spline Couplings
There are various types of spline couplings. These couplings have several important properties. These properties are: Stiffness, Involute splines, Misalignment, Wear and fatigue failure. To understand how these characteristics relate to spline couplings, read this article. It will give you the necessary knowledge to determine which type of coupling best suits your needs. Keeping in mind that spline couplings are usually spherical in shape, they are made of steel.
Involute splines
An effective side interference condition minimizes gear misalignment. When two splines are coupled with no spline misalignment, the maximum tensile root stress shifts to the left by five mm. A linear lead variation, which results from multiple connections along the length of the spline contact, increases the effective clearance or interference by a given percentage. This type of misalignment is undesirable for coupling high-speed equipment.
Involute splines are often used in gearboxes. These splines transmit high torque, and are better able to distribute load among multiple teeth throughout the coupling circumference. The involute profile and lead errors are related to the spacing between spline teeth and keyways. For coupling applications, industry practices use splines with 25 to fifty-percent of spline teeth engaged. This load distribution is more uniform than that of conventional single-key couplings.
To determine the optimal tooth engagement for an involved spline coupling, Xiangzhen Xue and colleagues used a computer model to simulate the stress applied to the splines. The results from this study showed that a “permissible” Ruiz parameter should be used in coupling. By predicting the amount of wear and tear on a crowned spline, the researchers could accurately predict how much damage the components will sustain during the coupling process.
There are several ways to determine the optimal pressure angle for an involute spline. Involute splines are commonly measured using a pressure angle of 30 degrees. Similar to gears, involute splines are typically tested through a measurement over pins. This involves inserting specific-sized wires between gear teeth and measuring the distance between them. This method can tell whether the gear has a proper tooth profile.
The spline system shown in Figure 1 illustrates a vibration model. This simulation allows the user to understand how involute splines are used in coupling. The vibration model shows four concentrated mass blocks that represent the prime mover, the internal spline, and the load. It is important to note that the meshing deformation function represents the forces acting on these three components.
Stiffness of coupling
The calculation of stiffness of a spline coupling involves the measurement of its tooth engagement. In the following, we analyze the stiffness of a spline coupling with various types of teeth using two different methods. Direct inversion and blockwise inversion both reduce CPU time for stiffness calculation. However, they require evaluation submatrices. Here, we discuss the differences between these two methods.
The analytical model for spline couplings is derived in the second section. In the third section, the calculation process is explained in detail. We then validate this model against the FE method. Finally, we discuss the influence of stiffness nonlinearity on the rotor dynamics. Finally, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method. We present a simple yet effective method for estimating the lateral stiffness of spline couplings.
The numerical calculation of the spline coupling is based on the semi-analytical spline load distribution model. This method involves refined contact grids and updating the compliance matrix at each iteration. Hence, it consumes significant computational time. Further, it is difficult to apply this method to the dynamic analysis of a rotor. This method has its own limitations and should be used only when the spline coupling is fully investigated.
The meshing force is the force generated by a misaligned spline coupling. It is related to the spline thickness and the transmitting torque of the rotor. The meshing force is also related to the dynamic vibration displacement. The result obtained from the meshing force analysis is given in Figures 7, 8, and 9.
The analysis presented in this paper aims to investigate the stiffness of spline couplings with a misaligned spline. Although the results of previous studies were accurate, some issues remained. For example, the misalignment of the spline may cause contact damages. The aim of this article is to investigate the problems associated with misaligned spline couplings and propose an analytical approach for estimating the contact pressure in a spline connection. We also compare our results to those obtained by pure numerical approaches.
Misalignment
To determine the centering force, the effective pressure angle must be known. Using the effective pressure angle, the centering force is calculated based on the maximum axial and radial loads and updated Dudley misalignment factors. The centering force is the maximum axial force that can be transmitted by friction. Several published misalignment factors are also included in the calculation. A new method is presented in this paper that considers the cam effect in the normal force.
In this new method, the stiffness along the spline joint can be integrated to obtain a global stiffness that is applicable to torsional vibration analysis. The stiffness of bearings can also be calculated at given levels of misalignment, allowing for accurate estimation of bearing dimensions. It is advisable to check the stiffness of bearings at all times to ensure that they are properly sized and aligned.
A misalignment in a spline coupling can result in wear or even failure. This is caused by an incorrectly aligned pitch profile. This problem is often overlooked, as the teeth are in contact throughout the involute profile. This causes the load to not be evenly distributed along the contact line. Consequently, it is important to consider the effect of misalignment on the contact force on the teeth of the spline coupling.
The centre of the male spline in Figure 2 is superposed on the female spline. The alignment meshing distances are also identical. Hence, the meshing force curves will change according to the dynamic vibration displacement. It is necessary to know the parameters of a spline coupling before implementing it. In this paper, the model for misalignment is presented for spline couplings and the related parameters.
Using a self-made spline coupling test rig, the effects of misalignment on a spline coupling are studied. In contrast to the typical spline coupling, misalignment in a spline coupling causes fretting wear at a specific position on the tooth surface. This is a leading cause of failure in these types of couplings.
Wear and fatigue failure
The failure of a spline coupling due to wear and fatigue is determined by the first occurrence of tooth wear and shaft misalignment. Standard design methods do not account for wear damage and assess the fatigue life with big approximations. Experimental investigations have been conducted to assess wear and fatigue damage in spline couplings. The tests were conducted on a dedicated test rig and special device connected to a standard fatigue machine. The working parameters such as torque, misalignment angle, and axial distance have been varied in order to measure fatigue damage. Over dimensioning has also been assessed.
During fatigue and wear, mechanical sliding takes place between the external and internal splines and results in catastrophic failure. The lack of literature on the wear and fatigue of spline couplings in aero-engines may be due to the lack of data on the coupling’s application. Wear and fatigue failure in splines depends on a number of factors, including the material pair, geometry, and lubrication conditions.
The analysis of spline couplings shows that over-dimensioning is common and leads to different damages in the system. Some of the major damages are wear, fretting, corrosion, and teeth fatigue. Noise problems have also been observed in industrial settings. However, it is difficult to evaluate the contact behavior of spline couplings, and numerical simulations are often hampered by the use of specific codes and the boundary element method.
The failure of a spline gear coupling was caused by fatigue, and the fracture initiated at the bottom corner radius of the keyway. The keyway and splines had been overloaded beyond their yield strength, and significant yielding was observed in the spline gear teeth. A fracture ring of non-standard alloy steel exhibited a sharp corner radius, which was a significant stress raiser.
Several components were studied to determine their life span. These components include the spline shaft, the sealing bolt, and the graphite ring. Each of these components has its own set of design parameters. However, there are similarities in the distributions of these components. Wear and fatigue failure of spline couplings can be attributed to a combination of the three factors. A failure mode is often defined as a non-linear distribution of stresses and strains.


China Standard Black OEM Motorcycles Gear Shaft, Worm Gear Shaft with Great quality
Product Description
Product Motorcycles Gear Shaft Pictures
Product Details
| Name |
Motorcycles gear shaft |
| Length |
3-2000mm,; and other length can be made for you |
| OEM/ODM |
We can custimize all types according to customers’ drawings or samples |
| Head |
Flat head/countersunk head/T head and so on |
| Diameter |
M2-M30,; other size can be made |
| MOQ | 1000pcs |
| Application |
Mechanical equipment,;tele-communications equipments,;robot,;computer cases and cabinet,;electrical appliances |
| Surface finishing |
Zn-plated,;ni-plated,;tin-plated,;chrome plated,;passivated,;sandblast and anodize,;chromate,;polish,;electro painting,;black anodize,;plain,;H.;D.;G,;etc.; |
| This product material |
Stainless steel/carbon steel and so on |
| Other available materials | 1.;Stainless steel:;SS302,;SS303,;SS316,;SS410,;SS420,;SS430,;etc.; |
| 2.;Steel:;C45(K1045);,;C46(K1046);,;C20,;etc.; |
|
| 3.;Brass or brass alloy:;H63;H65;H68;H70;H90,;etc.; |
|
| 4.;Bronze:;C51000,;C52100,;C54400,;etc |
|
| 5.;Iron:;1213,;1214,;1215,;etc.; |
|
| 6.;Aluminum or alumium alloy:;AI6061,;AI6063,;etc.; |
|
| 7.;Carbon steel:;C1006,;C1008,;C1571,;C1018A,;C1571,;C1035K,;C1045K,;etc.; |
|
| 8.;Titanium or titanium alloy:;TAD,;TA1-TA8,;TB2,;TC1-TC10,;etc.; |
|
| 9.;Silver or silver alloy:;AgCu3,;AgCu7.;5,;AgSn3-5,;AgPb0.;4-0.;7,;AgPd3-5,;AgNi10,;etc.; |
|
| 10.;Alloy steel:; SCM435,;10B21,;40Cr,;etc.; |
Production Process
Packaging Details
| Packing
|
Inside poly bags packing and the standard export packing or according to customer’s requirement |
| Delivery time |
Regular product is about 5-20days,; custom product will according to special requirement.; |
Company Profile
HangZhou Wanjin Hardware Products Co.;,; Ltd.; is specialized in non-standard parts manufacturer,; located in China.;
Our products include long screws,; long bolts,; CNC lathe parts,; stamping parts.; The applictaions include New energy,; Automotive,; Motor mechanical and electrical,; sports equipment,; Mechanical equipment,; baby products,; household appliances,; furniture,; electronic products.;
We have our own R & D team,; we have 2 design engineers and 5 technology developers.; Our engineers have 20 years of experience in designing,; developing and manufacturing a variety of non-standard custom fasteners.;
Our company strict implementation of I S O quality management.; We are direct custom production of non-standard screw fastener factory.; We can customize any kind of screws according to your design.; We provide all kinds of OEM,; design services,; buyer label services.; We have a complete foreign trade service team providing 24-hour online service.; We provide life-long service,; as long as you are our customers,; we will do our best to help you to solve the problem.;
Factory Equipment
Our factory’s equipment is very completed and good for quality.; We have image tester,; head machine,; falt milling machine,; driller,; HRC&HRB machine and so on,; welcome to cheack our factory and machine.;
Company Certification
Our products meet the standard of SGS,; ISO,; ROHS AND so on certifications,; some pictures of certificates for your check as follow
FAQ
1.;You are a manufacturing company or trading company?
—We are manufacturer.; So our prices are very reasonable.;
2.;What quote do you offer?
—FOB ,; CIF and others ways according the your needs.;
3.;How pay?
—All of kinds Payment we all accept from you
4.;How transport?
—Sea Freight,; Air Freight and others Express Delivery ways for you.;
5.;Can I order a small list ?
—Of course,;you can.;
6.;Can we print our own logo ?
—Yes,; we can print logo for you.;
7.;What is the quality of your products guarantee?
—We have passed ISO9001:;2008 Quality Management System Certification,;
CQM Quality Management System Certification and
IQNet Quality Management System Certification,;
If the quality doesn’t accord the standard,; you can exchange the goods for free.;
8.;Do you have after-sales service?
—Certainly,;you can contact us at any time.;
Types of Splines
There are 4 types of splines: Involute, Parallel key, helical, and ball. Learn about their characteristics. And, if you’re not sure what they are, you can always request a quotation. These splines are commonly used for building special machinery, repair jobs, and other applications. The CZPT Manufacturing Company manufactures these shafts. It is a specialty manufacturer and we welcome your business.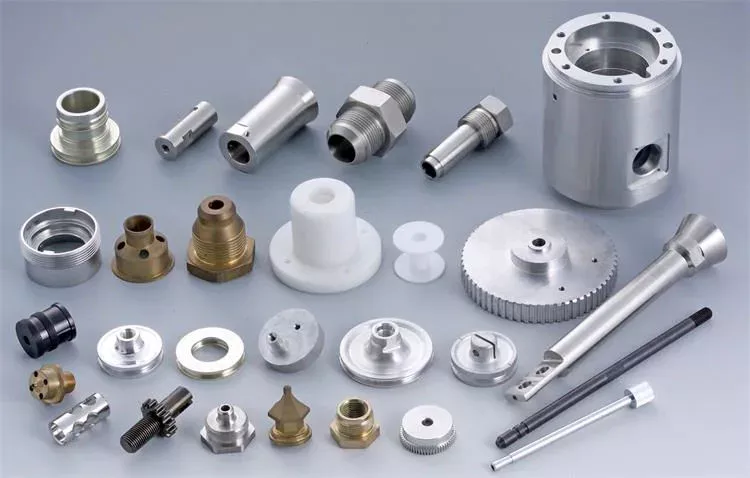
Involute splines
The involute spline provides a more rigid and durable structure, and is available in a variety of diameters and spline counts. Generally, steel, carbon steel, or titanium are used as raw materials. Other materials, such as carbon fiber, may be suitable. However, titanium can be difficult to produce, so some manufacturers make splines using other constituents.
When splines are used in shafts, they prevent parts from separating during operation. These features make them an ideal choice for securing mechanical assemblies. Splines with inward-curving grooves do not have sharp corners and are therefore less likely to break or separate while they are in operation. These properties help them to withstand high-speed operations, such as braking, accelerating, and reversing.
A male spline is fitted with an externally-oriented face, and a female spline is inserted through the center. The teeth of the male spline typically have chamfered tips to provide clearance with the transition area. The radii and width of the teeth of a male spline are typically larger than those of a female spline. These specifications are specified in ANSI or DIN design manuals.
The effective tooth thickness of a spline depends on the involute profile error and the lead error. Also, the spacing of the spline teeth and keyways can affect the effective tooth thickness. Involute splines in a splined shaft are designed so that at least 25 percent of the spline teeth engage during coupling, which results in a uniform distribution of load and wear on the spline.
Parallel key splines
A parallel splined shaft has a helix of equal-sized grooves around its circumference. These grooves are generally parallel or involute. Splines minimize stress concentrations in stationary joints and allow linear and rotary motion. Splines may be cut or cold-rolled. Cold-rolled splines have more strength than cut spines and are often used in applications that require high strength, accuracy, and a smooth surface.
A parallel key splined shaft features grooves and keys that are parallel to the axis of the shaft. This design is best suited for applications where load bearing is a primary concern and a smooth motion is needed. A parallel key splined shaft can be made from alloy steels, which are iron-based alloys that may also contain chromium, nickel, molybdenum, copper, or other alloying materials.
A splined shaft can be used to transmit torque and provide anti-rotation when operating as a linear guide. These shafts have square profiles that match up with grooves in a mating piece and transmit torque and rotation. They can also be easily changed in length, and are commonly used in aerospace. Its reliability and fatigue life make it an excellent choice for many applications.
The main difference between a parallel key splined shaft and a keyed shaft is that the former offers more flexibility. They lack slots, which reduce torque-transmitting capacity. Splines offer equal load distribution along the gear teeth, which translates into a longer fatigue life for the shaft. In agricultural applications, shaft life is essential. Agricultural equipment, for example, requires the ability to function at high speeds for extended periods of time.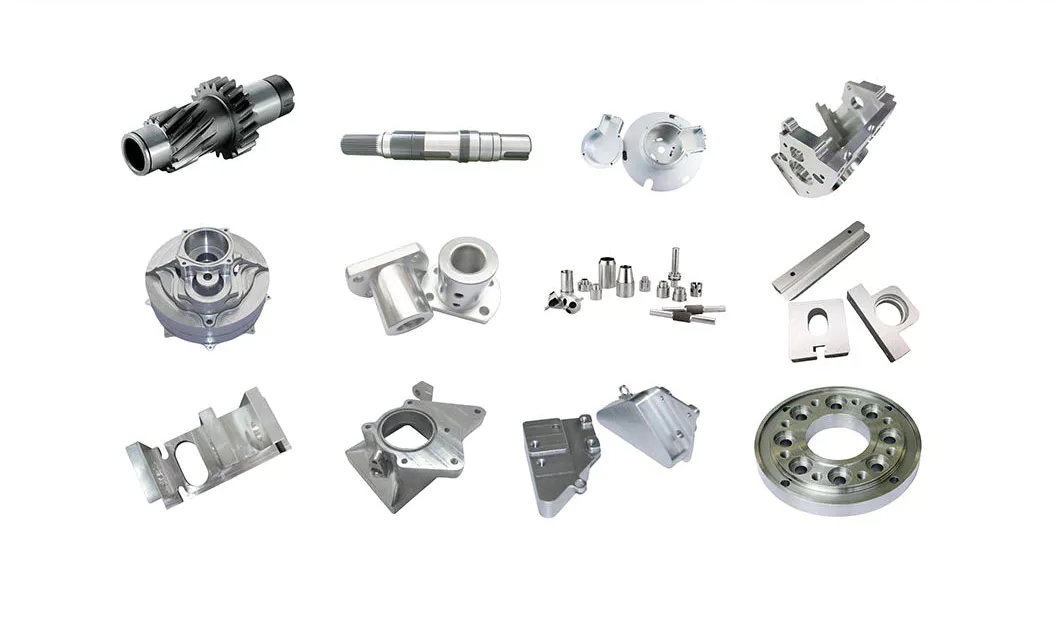
Involute helical splines
Involute splines are a common design for splined shafts. They are the most commonly used type of splined shaft and feature equal spacing among their teeth. The teeth of this design are also shorter than those of the parallel spline shaft, reducing stress concentration. These splines can be used to transmit power to floating or permanently fixed gears, and reduce stress concentrations in the stationary joint. Involute splines are the most common type of splined shaft, and are widely used for a variety of applications in automotive, machine tools, and more.
Involute helical spline shafts are ideal for applications involving axial motion and rotation. They allow for face coupling engagement and disengagement. This design also allows for a larger diameter than a parallel spline shaft. The result is a highly efficient gearbox. Besides being durable, splines can also be used for other applications involving torque and energy transfer.
A new statistical model can be used to determine the number of teeth that engage for a given load. These splines are characterized by a tight fit at the major diameters, thereby transferring concentricity from the shaft to the female spline. A male spline has chamfered tips for clearance with the transition area. ANSI and DIN design manuals specify the different classes of fit.
The design of involute helical splines is similar to that of gears, and their ridges or teeth are matched with the corresponding grooves in a mating piece. It enables torque and rotation to be transferred to a mate piece while maintaining alignment of the 2 components. Different types of splines are used in different applications. Different splines can have different levels of tooth height.
Involute ball splines
When splines are used, they allow the shaft and hub to engage evenly over the shaft’s entire circumference. Because the teeth are evenly spaced, the load that they can transfer is uniform and their position is always the same regardless of shaft length. Whether the shaft is used to transmit torque or to transmit power, splines are a great choice. They provide maximum strength and allow for linear or rotary motion.
There are 3 basic types of splines: helical, crown, and ball. Crown splines feature equally spaced grooves. Crown splines feature involute sides and parallel sides. Helical splines use involute teeth and are often used in small diameter shafts. Ball splines contain a ball bearing inside the splined shaft to facilitate rotary motion and minimize stress concentration in stationary joints.
The 2 types of splines are classified under the ANSI classes of fit. Fillet root splines have teeth that mesh along the longitudinal axis of rotation. Flat root splines have similar teeth, but are intended to optimize strength for short-term use. Both types of splines are important for ensuring the shaft aligns properly and is not misaligned.
The friction coefficient of the hub is a complex process. When the hub is off-center, the center moves in predictable but irregular motion. Moreover, when the shaft is centered, the center may oscillate between being centered and being off-center. To compensate for this, the torque must be adequate to keep the shaft in its axis during all rotation angles. While straight-sided splines provide similar centering, they have lower misalignment load factors.
Keyed shafts
Essentially, splined shafts have teeth or ridges that fit together to transfer torque. Because splines are not as tall as involute gears, they offer uniform torque transfer. Additionally, they provide the opportunity for torque and rotational changes and improve wear resistance. In addition to their durability, splined shafts are popular in the aerospace industry and provide increased reliability and fatigue life.
Keyed shafts are available in different materials, lengths, and diameters. When used in high-power drive applications, they offer higher torque and rotational speeds. The higher torque they produce helps them deliver power to the gearbox. However, they are not as durable as splined shafts, which is why the latter is usually preferred in these applications. And while they’re more expensive, they’re equally effective when it comes to torque delivery.
Parallel keyed shafts have separate profiles and ridges and are used in applications requiring accuracy and precision. Keyed shafts with rolled splines are 35% stronger than cut splines and are used where precision is essential. These splines also have a smooth finish, which can make them a good choice for precision applications. They also work well with gears and other mechanical systems that require accurate torque transfer.
Carbon steel is another material used for splined shafts. Carbon steel is known for its malleability, and its shallow carbon content helps create reliable motion. However, if you’re looking for something more durable, consider ferrous steel. This type contains metals such as nickel, chromium, and molybdenum. And it’s important to remember that carbon steel is not the only material to consider.

